|
Common Name: |
Bentazone
|
|
Chemical Name: |
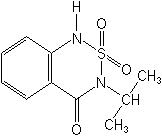
3-isopropyl-1H-2,1,3-benzothiadiazin-4(3H)-one
2,2-dioxide
|
|
CAS No.: |
25057-89-0
|
| Structure: |
 |
|
Molecular Formula: |
C10H12N2O3S
|
|
Molecular Weight: |
240.2
|
|
Physical Chemistry: |
Pure
Bentazon is a colorless to slightly brown, odorless crystalline
solid. Water Solubility:
500 mg/L @ 20 C.
Solubility in Other Solvents: acetone v.s.; ethanols,
ethyl acetates, and benzene s.s.; cyclohexane s.s.
Melting Point:
137-139 C.Vapor Pressure:
Negligible; <0.46 mPa @ 20 C
|
|
Toxicity: |
The
LD50 for bentazon in rats is 1100 to 2063 mg/kg . Its dermal LD50 is
4000 mg/kg in rabbits. When bentazon was applied to the shaven skin
of rabbits, it did not cause irritation.
|
|
Application: |
Bentazon is a post-emergence herbicide used for selective control of
broadleaf weeds and sedges (a weed) in beans, rice, corn, peanuts,
mint, and others. Bentazon is a contact herbicide, which means that
it causes injury only to the parts of the plant to which it is
applied. It interferes with the ability of susceptible plants to use
sunlight for photosynthesis.
|
|
Technical Purity: |
95%Tech
|
|
Formulation Type: |
48%SL
|
|



