| Common
Name: |
Metaldehyde
|
| Chemical
Name: |
2,4,6,8-tetramethyl-1,3,5,7-tetraoxacyclooctane
|
| CAS
No.: |
108-62-3
|
| Structure: |
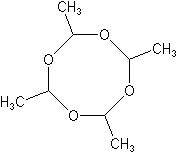 |
| Molecular
Formula: |
C8H16O4
|
| Molecular
Weight: |
176.20
|
| Physical
Chemistry: |
Metaldehyde
is a white or colorless crystalline solid with a mild characteristic
odor and a powdery appearance. Water Solubility: 260 mg/L @
30 C. Solubility in Other Solvents: i.s. in acetic acid; s. in hot
carbon disulfide; s. in ethyl alcohol; v.s. in benzene and
chloroform; s.s. in ethanol and diethyl ether. Melting Point:
Sublimes at approx. 112 C. Vapor Pressure: Negligible at room
temperature. Adsorption Coefficient: 240.
|
| Toxicity: |
Metaldehyde is slightly to moderately
toxic by ingestion, with reported oral LD50 values of 227 to 690
mg/kg in rats. Via the dermal route, it is also moderately toxic.
The dermal LD50 for this molluscicide in rats is from 2275 mg/kg to
greater than 5000 mg/kg. Metaldehyde is moderately toxic by
inhalation; the 4-hour inhalation LC50 in rats is 0.2 mg/L, and the
2-hour inhalation LC50 in mice is 0.35 mg/L. Irritation of the skin,
eye, and mucous membranes of the upper airways and gastrointestinal
tract may result from contact with metaldehyde.
|
| Application: |
Metaldehyde is a molluscicide used in a variety of
vegetable and ornamental crops in the field or greenhouse, on fruit
trees, small-fruit plants, or in avocado or citrus orchards, berry
plants, and banana plants. It is used to attract and kill slugs and
snails. It is applied in the form of granules, sprays, and dusts, or
pelleted or grain bait, typically to the ground around the plants or
crops. It works primarily in the stomach by producing toxic effects
after it is ingested by the pest.
|
| Technical
Purity: |
99%Tech
|
| Formulation
Type: |
6%GB, 5%GB
| |



